Explore the sine, cosine, and tangent of complementary angles within right triangles.
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Provider:
- CK-12 Foundation
- Date Added:
- 05/07/2018

Explore the sine, cosine, and tangent of complementary angles within right triangles.
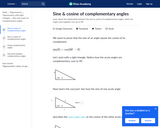
On this webpage, students learn about the relationship between the sine and cosine of complementary angles, which are angles who together sum up to 90°.

Students examine the sine and cosine relationship more closely and find that the sine and cosine of complementary angles are equal. Students become familiar with the values associated with sine and cosine of special angles.

The purpose of this task is to lead students through an algebraic approach to a well-known result from classical geometry, namely, that a point X is on the circle of diameter AB whenever ∠AXB is a right angle. This consists of translating the right-angle condition into the negative reciprocal slope property of perpendicular lines, followed by a short series of algebraic manipulations (principally, completing the square).

Students experience modeling a real-world example of exponential growth, in a context that provides a vivid illustration of the power of exponential growth, for example the cost of inaction for a year.
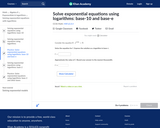
In this Khan Academy activity, students will solve exponential equations using logarithms.
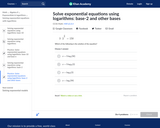
In this Khan Academy activity, students will solve exponential equations using logarithms.
Students are introduced to the formal process of solving an equation: starting from the assumption that the original equation has a solution. Students explain each step as following from the properties of equality. Students identify equations that have the same solution set.
This video solves the equation, by estimation, e^x=1/[x(x-1)(x-2)] by considering the graphs of y=e^x and y=1/[x(x-1)(x-2)].
This video solves the equation, with technology, e^x=1/[x(x-1)(x-2)] by considering the graphs of y=e^x and y=1/[x(x-1)(x-2)].
In this article, students learn a clever method for approximating the solution of any equation.
Students apply properties of logarithms to solve exponential equations. Students relate solutions to f(x) = g(x) to the intersection point(s) on the graphs of y = f(x) and y = g(x) in the case where f and g are constant or exponential functions.

Notes on Solving exponential equations

This website shows how to solve exponentials using logarithms and provides examples and practice problems.
This resource provides an explanation of solving exponential and logarithmic equations and practice problems.

Notes on solving logarithm Equations

Students solve simple logarithmic equations using the definition of logarithm and logarithmic properties.
Video that discusses the exact order of steps in the process of solving the equation 3(x+6)^2=75.

Four practice worksheets with word problems on radical equations and their solutions.

Filled in notes with vocabulary and example problems with radical equations.