
Guided notes for class use with vocabulary on solving radical equations.
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Lesson Plan
- Provider:
- Deer Valley Unified School District
- Date Added:
- 07/02/2018

Guided notes for class use with vocabulary on solving radical equations.

Worksheet solving rational equations

The purpose of this task is twofold. First, it prompts students to notice and explain a connection between the factored form of a polynomial and the location of its zeroes when graphed. Second, it highlights a complication that results from a seemingly innocent move that students might be tempted to make: "dividing both sides by x."
Students learn if-then moves using the properties of equality to solve equations. Students also explore moves that may result in an equation having more solutions than the original equation.

This lesson unit is intended to help you assess how well students are able to: Use the Pythagorean theorem to derive the equation of a circle.
Translate between the geometric features of circles and their equations.
Texas Instrument Activity. Students will construct and explore medians, altitudes, angle bisectors, and perpendicular bisectors of triangles. They then drag the vertices to see where the intersections of the segments lie in relation to the triangle, and they measure distances to identify relationships.

Surface Area and Volume of spheres worksheet.
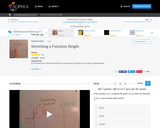
In this lesson the vertical stretching or squishing of a function on a graph is demonstrated.
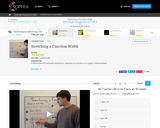
In this lesson the horizontal stretching or squishing of a function on a graph is demonstrated.
Students extend what they learned in Module 3 about how multiplying the parent function by a constant or multiplying the x-values of the parent function results in the shrinking or stretching (scaling) of the graph of the parent function and, in some cases, results in the reflection of the function about the x- or y-axis.
In this activity, students will understand the process of making inferences about a populations based on a random sample from that population. They will also recognize the purpose of and the differences between sample surveys, experiments, and observational studies and understand how randomization should be used in each.

This video shows how to subtract two functions.

This video shows how to rewrite (-5x)/(8x+7)-(6x^3)/(3x+1) as (-48x^4-42x^3-15x^2-5x)/(8x+7)(3x+1).

The intent of this problem is to have students think about how function addition works on a fundamental level, so formulas have been omitted on purpose. In the graph shown, g(x)=4x2+1. The task may be extended by asking students to sketch the graph of d(x)=f(x)−g(x).

This tutorial covers dividing a polynomial by a binomial of the form x-c using synthetic division, using the Remainder Theorem in conjunction with synthetic division to find a functional value, and using the Factor theorem in conjunction with synthetic division to find factors and zeros of a polynomial function.

Practice with systems of linear equations.
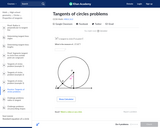
In this Khan Academy activity, students will solve different problems that involve the tangent of a circle.

Practice working with tangent lines to circles.

The first part of this task provides an opportunity to construct a linear function given two input-output pairs. The second part investigates the inverse of a linear function while the third part requires reasoning about quantities and/or solving a linear equation.

This task has a couple of aspects designed to encourage students to attend to the structure of the equation and the meaning of the variables in it. By focusing on different variables in parts (a) and (b), it fosters flexibility in seeing the same equation in two different ways: first as an equation in t with constants v and d, then as an equation in v with constants t and d.