This video solves the following equation and eliminates the resulting extraneous solution: (x^2)/(x+2)=4/(x+2).
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Demonstration
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Date Added:
- 03/16/2018

This video solves the following equation and eliminates the resulting extraneous solution: (x^2)/(x+2)=4/(x+2).
In this Khan Academy activity, students will determine which expressions are equivalent to a given exponential expression.
In this Khan Academy activity, students will evaluate expressions using structure.
In this Khan Academy activity, students will evaluate logarithms using the change of base rule.
In this Khan Academy activity, students will practice evaluating piecewise functions.

Starting with explicit cases, this task derives the formula for an arbitrary circle in the plane.
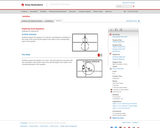
Students will discover the equation of circles of the form (x – h)^2+ (y – k)^2= r^2, where (h, k) is the center of the circle and r is the radius of the circle.
This lesson will provide real world examples that involve setting up and solving for an exponential decay problem.
This video models a context that concerns a bank savings account. The model turns out to be an exponential equation.
Practice writing exponential functions from tables and graphs.
In this lesson, students compare linear and exponential models of population growth.

This problem shows that an exponential function takes larger values than a cubic polynomial function provided the input is sufficiently large.
This lesson will provide real world examples that involve setting up and solving for an exponential growth problem.
The purpose of this task is twofold: first using technology to study the behavior of some exponential and logarithmic graphs and secondly to manipulate some explicit logarithmic and exponential expressions.
In this Khan Academy activity, students will evaluate exponential word problems.
Students will determine that the inverse of the exponential function is the natural log function by plotting the inverse of exponential solution points.

The purpose of this task is to help students see that the definition of the logarithm as an exponent results in an inverse relationship between the exponential and logarithm functions with the same base. This prepares them to think about the shape of the graph of the logarithm function in terms of the shape of the graph of the exponential function.
This lesson will show you how to use the proper formula and rewrite an equation as a logarithm and then again as an expression with an exponent.

The goal of this task is to examine how extraneous solutions can arise when solving rational equations.
Students learn how to find and label extrema using first and second derivatives, be able to inspect a graph and determine which extrema the function has, and be able to use trace, fMin, and fMax to verify the computed answers and find critical values for parametric functions.