
Practice problems using the fundamental theorem of algebra on polynomial equations.
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Provider:
- Kuta Software
- Date Added:
- 03/01/2018

Practice problems using the fundamental theorem of algebra on polynomial equations.

Worksheet using the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
Students examine the relationship between a cross-section and the base of a general cone. Students understand that pyramids and circular cones are subsets of general cones just as prisms and cylinders are subsets of general cylinders.
Students are reintroduced to several solids as a lead into establishing the volume formulas for the figures. They also identify the three-dimensional object generated by the rotation of a rectangular region about an axis
Students simulate a geometric distribution of rolling a die to determine experimental probabilities and calculate theoretical probabilities.
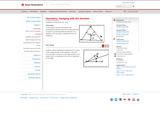
Students will explore the perpendicular bisector theorem and discover that if a point is on the perpendicular bisector of a segment, then the point is equidistant from the endpoints.
In this activity, students apply the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra in determining the complex roots of polynomial functions. The theorem is applied both algebraically and graphically.
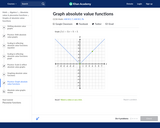
In this Khan Academy activity, students will graph absolute value functions.
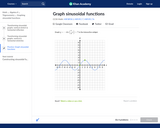
In this Khan Academy activity, students will graph a sinusoidal function.
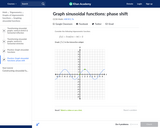
In this Khan Academy activity, students will graph a sinusoidal function with a phase shift.
In this Khan Academy activity, students will graph a circle from its expanded equation.
In this Khan Academy activity, students will graph a circle from its features.
In this Khan Academy activity, students will graph a circle from its standard equation.

In this Khan Academy activity, students will graph exponential growth and decay problems.

Notes that help students chose the method for solving a polynomial.
Students explore the key features of the graphs of rational functions and use the intercepts and asymptotes to create graphs of rational functions without using technology
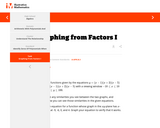
The purpose of this task is to help students understand the relationship between the factors of a polynomial and the x-intercepts of the graph of the polynomial.
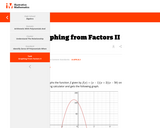
The purpose of this task is to give students an opportunity to see and use the structure of the factored form of a polynomial. The factor x−50 tells them that they should include x=50 in the range on the x-axis. Students might also draw on their knowledge of the long run behavior of a cubic polynomial to recognize that Emery's graph must eventually return across the x-axis to the right of his current viewing window.
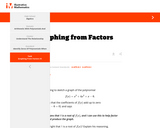
The task has students use the remainder theorem to deduce a linear factor of a cubic polynomial, and then to completely factor the polynomial. Students will need some procedure (e.g., synthetic or long division, or guess-and-check the coefficients) for determining the quadratic factor. Having the factored form permits students to deduce much about the structure of the graph.
Students discover the key features of the sine and cosine functions and to connect the graphs to the measurements on the unit circle.