This video shows an example of how to use the median and centroid properties to solve a problem.
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Demonstration
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Date Added:
- 03/19/2018

This video shows an example of how to use the median and centroid properties to solve a problem.

This task addresses the first part of standard F-BF.3: “Identify the effect on the graph of replacing f(x) by f(x)+k, kf(x), f(kx), and f(x+k) for specific values of k (both positive and negative). Here, students are required to understand the effect of replacing x with x+k, but this task can also be modified to test or teach function-building skills involving f(x)+k, kf(x), and f(kx) in a similar manner.
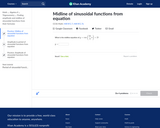
In this Khan Academy activity, students will identify the midline of sinusoidal functions from an equation.
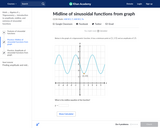
In this Khan Academy activity, students will identify the midline of sinusoidal functions from a graph.
This website shows how to prove a theorem about quadrilaterals and parralelograms.

The problem requires students at times to see the denominator as a single entity, representing the total volume of the solutions, and at other times to see it as sum of two other entities, representing the volume of the water and the volume of the fertilizer.
Students use simulations and graphs to explore what happens when the number of trials of a binomial experiment becomes a large number.
Students write equations to model data from tables, which can be represented with linear, quadratic, or exponential functions, including several from Lessons 4 and 5. They recognize when a set of data can be modeled with a linear, exponential, or quadratic function and create the equation that models the data. Students interpret the function in terms of the context in which it is presented, make predictions based on the model, and use an appropriate level of precision for reporting results and solutions.
Students create a two-variable equation that models the graph from a context. Function types include linear, quadratic, exponential, square root, cube root, and absolute value. They interpret the graph, function, and answer questions related to the model, choosing an appropriate level of precision in reporting their results
Students will be able to create exponential functions to model real-world situations, use logarithms to solve equations of the form f(t) = a · b^(ct) for t, and decide which type of model is appropriate by analyzing numerical or graphical data, verbal descriptions, and by comparing different data representations.
In this Khan Academy activity, students will model word problems with sinusoidal functions that have a phase shift.

Worksheet on factoring and finding zeros of a polynomial and building polynomials given its zeros.
In this Prezi, students learn about simplifying, multiplying, and dividing rational expressions.
This video shows how to multiply two functions.

This video multiplies and simplifies (3x^2y)/(2ab) X (14a^2b)/(18xy^2).
This lesson depicts how to take the product of the x expressions from two functions and distribute and combine like terms.
In this article, students see how they can multiply or divide two functions to create a new function.

This resource provides an explanation on multiplying and dividing rational expressions and 56 practice questions with solutions.
This video multiplies (6x^3/5) X (2/3x) and divides (2x^4/7) by (5x^4/4).
This is a challenging task which requires students to carefully divide up the picture into different pieces for which the area is known.