Students will explore the connection between exponential growth and geometric sequences and to compare linear growth to exponential growth in context.
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Lesson Plan
- Provider:
- EngageNY
- Date Added:
- 02/02/2018

Students will explore the connection between exponential growth and geometric sequences and to compare linear growth to exponential growth in context.
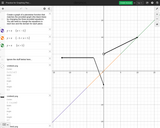
Interactive resources that allows the user to manipulate characteristics of a piecewise function to graph.
Students use the random integer (randInt) command to simulate probability experiments. They also graph the number of trials and corresponding probabilities to observe the Law of Large Numbers. Simulated experiments involve tossing a coin, spinning a spinner, and observing the sex of children in a family.

The purpose of this task is to test student skill at converting verbal statements into two algebraic equations and then solving those equations. The student should assign variables to each number, form the system of the two equations, and solve the system. The final step is to add the values found for the two assigned variables. This problem is different from many that students have seen since the two equations are not linear. One way to solve such a system is by substitution: this is presented in the first solution though students might choose a different way to perform the substitution since either of the given equations can be solved for x in terms of y or for y in terms of x. A second solution is presented where the two equations are manipulated in a different way.

Student project based on earning and paying compound interest
This video shows that a figure is a parallelogram if and only if opposite sides are congruent.
This video goes over the proof of the Remainder Theorem.
Students complete proofs that incorporate properties of parallelograms.

Practice problems applying properties of parallelograms to solve problems.

The goal of this task is to use the unit circle and rigid transformations in order to establish some fundamental trigonometric function identities.
This video models a context that concerns a candy vending machine. The model turns out to be a quadratic inequality.
This video solves the system y=x+1 and x^2+y^2=25.
This video solves a system of a quadratic equation and a linear equation by graphing both equations and looking for their intersections, and then checks the solution algebraically.
This video shows that the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra holds for polynomials of the second degree.
Video that analyzes a given solution of a quadratic equation, and finds where and what was the error in that process.
This question provides students with an opportunity to see expressions as constructed out of a sequence of operations: first taking the square root of n, then dividing the result of that operation into s.
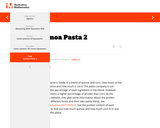
Students must come up with the idea on their own that they can set up two equations in two unknowns to solve the problem, and they must then read, understand and extract information from the nutrition labels to set up the equations in the system. The algebra needed to solve the system is fairly simple substitution; the main difficulty lies in the modeling aspect.
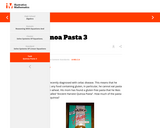
This task is an example of a mathematical modeling problem and it also illustrates making sense of a problem. Students are only told that there are two ingredients in the pasta and they have a picture of the box. It might even be better to just show the picture of the box, or to bring in the box and ask the students to pose the question themselves. The box has the nutritional label and a reference to the website where the students can find other information about the ingredients. (The brand of pasta is quite commonly available at supermarkets or health food stores such as Whole Foods and even at Amazon.com.)

Worksheet with problems involving radian measure.

This resource covers measuring angles in radians, converting angles from degrees to radians, converting angles from radians to degrees, calculating the length of an arc of a circle, calculating circular speeds, calculating the area of a sector of a circle, and calculating the area of a segment of a circle.