
How to measure Juncos "Boldness" will be discussed.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Science
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Provider:
- iHub
- Date Added:
- 08/29/2019

How to measure Juncos "Boldness" will be discussed.
Develop a model: what are bird responses to approaching human(s)?

Flight Initiation Distance (FID) was recorded for both foraging birds and incubating females in the field.
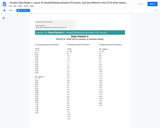
The chart shows the results and raw data for the juncos behavior.

The graph displayed shows relative flight distance of birds vs. the number of generations since the birds have been present in urban areas. Each data point represents a different kind of bird, and the line is a linear regression line for this data.

Visual representation of measurable bird behavior responses to an approaching human is shown in this chart.
Do you think our natural selection model can be used to explain how the UCSD juncos became bolder in that environment or do you think some aspects of the model will need to be revised?
We can test if a behavior is inherited or learned by taking some individuals born into one enviornment and raising them in a different environment and seeing what traits change and which ones stay the same.

How scientists determine learned vs inherited behavior will be discussed.
Follow all procedures to develop a working model for the juncos behavior being learned or inherited. This lesson has several readings for guidance on protocol.

Little is known about the molecular basis of differences in behavior among individuals. Here we report consistent novelty-seeking behavior, across different contexts, among honey bees in their tendency to scout for food sources and nest sites, and we reveal some of the molecular underpinnings of this behavior relative to foragers that do not scout. Note: this reading coincides with Student Activity Sheets.

A respected scientist named Hans Kummer was working in a region containing two species of baboons with very different social systems. Savanna baboons live in large troops, with plenty of adult females and males. Hamadryas baboons, in contrast, have a more complex, multilevel society. Note: this reading coincides with Student Activity Sheets.

Time line of Addie's case.

Create a model for Addie's sickness.
You will watch a video clip (13 mins long) that will introduce you to the case of a little girl who also got sick and went to the doctor to get medicine to help her get better.

Throughout our investigation of Addie’s case, we will be using the Incremental Modeling Tracker (IMT) as a thinking tool to help you keep track of and figure out important discoveries. You will refer back to the IMT regularly to help prioritize ideas and revise or build on our models for what’s going on with Addie. We will also use the IMT as a way to think with others about what is important in our models.
Exploratory behavior in juncos is inherited. Alleles that are or are not inherited can influence what substances are or are not produced by cells in any living creature. We think this might be what is causing differences in their behavior.

The relationship between a bird's Flight Inhibition Distance and exploratory behavior will be discussed.
Consider what Flight Initiation Distance and Exploratory Behavior actually mean for the birds in the two populations.
In stressful situations the amount of stress hormone in the blood stream is different for juncos from these different populations. This is correlated to the amount of exploratory behavior they engage in. The variation in this physiological mechanism is heritable, which leads to variation in behavior between juncos.