In this simulation activity, students will examine natural selection in a small population of wild rabbits.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Science
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Provider:
- PBS
- Author:
- WGBH
- Date Added:
- 02/26/2019

In this simulation activity, students will examine natural selection in a small population of wild rabbits.

In this biology lesson with math and ELA integration, students use real rock pocket mouse data to illustrate the Hardy-Weinberg principle.
This activity presents a fun, collaborative and interdisciplinary way to get students excited about the study of human genetics. Students pair up to create a genetic portrait of their imaginary family based on several observable, heritable traits. By actively using their knowledge, students will appreciate the importance and meaning of the study of genetics in its real-life context.

After completing this lesson, students will have a better grasp of genetic terminology such as genotype, phenotype, carrier, homozygous, heterozygous, autosomal, dominant, and recessive. Students will also become more competent in using Punnett squares to predict traits in offspring (cystic fibrosis (CF) status in this case). Finally, after experiencing the difficulty of making a genetic decision, students will become more aware of the complexity of such bioethical decision making.

This fact sheet is a supplemental resource to be used in conjunction with the lesson "Am I a Carrier for Cystic Fibrosis?" After completing this lesson, students will have a better grasp of genetic terminology such as genotype, phenotype, carrier, homozygous, heterozygous, autosomal, dominant, and recessive. Students will also become more competent in using Punnett squares to predict traits in offspring (cystic fibrosis (CF) status in this case). Finally, after experiencing the difficulty of making a genetic decision, students will become more aware of the complexity of such bioethical decision making.

In the Animal Science course, students study large, small, and specialty animals. Students explore the necessary elements--such as diet, genetics, habitat, and behavior--to create humane, ecologically and economically sustainable animal production systems.

Students will observe Mendel's Laws of Segregation and Independent Assortment through a series of monohybrid crosses with Brassica rapa plants. Students will make inferences supporting Mendel's laws on the basis of their interpretation of the results of these crosses.

Students "breed" baby dragons using paper chromosomes to determine the genotype and phenotype.

In this lesson, students will be able to define selective breeding and describe how selective breeding changes a population over time.

In this lesson, students will research a variety of chromosomal abnormalities and resulting syndromes to determine risk factors and contributors of the abnormality, and characteristics of the syndromes.

This lesson emphasizes the relationship between DNA sequences, mutations in DNA and the change in the resulting protein structure and function. Hemophilia A will be used as a real life example of how a mutation in DNA results in a change in a protein's structure and resulting ability to function. In order to complete these activities, the students should have prior knowledge in DNA structure and mutations, protein synthesis, Mendelian genetics and sex-linked traits.

In this exercise, students review information about how color blindness is inherited and complete several problem solving exercises applying their knowledge.

In this lesson, students will participate in a natural selection simulation, flipping pennies to mimic the probability of passing on certain traits. The traits are the three genes for color-vision, found on the X chromosome. In the simulation, students will simulate six generations of primates, and track how the gene pool changes over time. The activity loosely mimics some of the mechanisms that led to the evolution of our own improved color vision.

In this exercise, students will use StarGenetics to analyze the nature and mode of inheritance of specific genetic traits.
In this lesson, students will discuss the pro's and con's of prenatal genetic testing. Then students will research a particular genetic disorder and create a pamphlet about the disorder from the point of view of a genetic counselor.

In this lesson, students learn how to make a karyotype, learn how to read a karyotype, and be able to identify conditions and syndromes exhibited by a karyotype. In addition, students will be able to describe symptoms that might be exhibited by these conditions or syndromes.

This presentation is a supplemental resource to be used in conjunction with the lesson "Cytogenetics." In this lesson, students learn how to make a karyotype, learn how to read a karyotype, and be able to identify conditions and syndromes exhibited by a karyotype. In addition, students will be able to describe symptoms that might be exhibited by these conditions or syndromes.

This presentation is a supplemental resource to be used in conjunction with the lesson "Cytogenetics." In this lesson, students learn how to make a karyotype, learn how to read a karyotype, and be able to identify conditions and syndromes exhibited by a karyotype. In addition, students will be able to describe symptoms that might be exhibited by these conditions or syndromes.
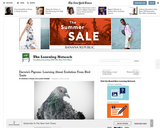
Students read an article describing a study that sheds new light on Charles Darwin's hobby of breeding pigeons. They learn about the origins of genes responsible for certain traits in pigeons, explore how scientists unravel the connections between genes and physical characteristics, and simulate a selective breeding program.

With this problem set, students can assess their understanding of the dihybrid cross. For each problem there is a tutorial feature that will explain the science behind the problem.