Students examine sequences and are introduced to the notation used to describe them.
- Subject:
- Math 1
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Author:
- EngageNY
- Date Added:
- 02/03/2020

Students examine sequences and are introduced to the notation used to describe them.
Students write sequences with recursive and explicit formulas.
Students understand that a function from one set (called the domain) to another set (called the range) assigns each element of the domain to exactly one element of the range and understand that if f is a function and x is an element of its domain, then f(x) denotes the output of corresponding to the input x.
Students use function notation, evaluate functions for inputs in their domains, and interpret statements that use function notation in terms of a context.
Students understand set builder notation for the graph of a real-valued function: {(x, f(x)) | x ∈ D}.
Students learn techniques for graphing functions and relate the domain of a function to its graph.
Students understand the meaning of the graph of y = f(x), namely {(x,y) | x ∈ D and y = f(x)}.
Students understand the definitions of when a function is increasing or decreasing.
Students use function notation, evaluate functions for inputs in their domains, and interpret statements that use function notation in terms of a context.
Students create functions that represent a geometric situation and relate the domain of a function to its graph and to the relationship it describes.
Students understand that a function from one set (called the domain) to another set (called the range) assigns each element of the domain to exactly one element of the range.
Students use function notation, evaluate functions for inputs in their domains, and interpret statements that use function notation in terms of a context.

Practice worksheet with word problems and reasonable domain and range
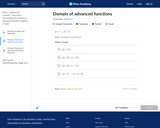
In this Khan Academy activity, students will practice finding the domain of advanced functions.
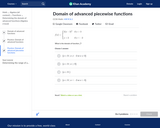
In this Khan Academy activity, students will practice finding the domain of advanced piecewise functions.
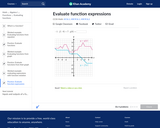
In this Khan Academy activity, students will practice evaluating function expressions given their graph.
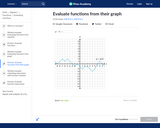
In this Khan Academy activity, students will practice evaluating function expressions given their graph.

In this lesson, students will learn to evaluate a function written as an expression by substituting a value into the given expression. Students will also learn that they can substitute another expression into the original expression of the function. They will recognize that g(x) is the output of a function and the expression x is the input. Students will also evaluate functions using tables and graphs.

The purpose of this task is to introduce the idea of the domain of a function by linking it to the evaluation of an expression defining the function. By thinking through the evaluation step by step, students isolate the exact point where a given input results in an undefined output.
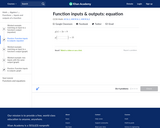
In this Khan Academy activity, students will practice determining what value should be inputted into a function to get the given output.
In this Khan Academy activity, students will practice finding the input value for a function from their graph.

Word problems writing equations, graphing functions and discussing reasonableness of answers.
In this Khan Academy activity, students will practice writing a formula for a function in terms of a given variable.

In this resource, students will determine if a relationship is a function and compare their rate of change and initial value.

This unit builds on the student's prior learning of how to find a rule that takes a given input value to exactly one output value. In this unit students will be able to identify when a relation is a function and use proper vocabulary (domain and range) and function notation.
Families of functions will be introduced in this unit including linear, absolute value, exponential and quadratic families of functions. Students will use graphs, tables and equations to identify the parent function and be able make a graph from the information in an equation and vice versa. This unit also introduces students to the concept of functions and their inverses. Students will write expressions for simple, linear functions that have an inverse.
Students will continue to use the concepts learned in this unit throughout the remainder of the course and in high school courses.