
Create a 3 dimensional model using known base shapes such as square or rectangle, circle or semi-circle
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Author:
- William Allred
- Carrie Robledo
- Date Added:
- 05/18/2021

Create a 3 dimensional model using known base shapes such as square or rectangle, circle or semi-circle

Student will be able to use integration and differentiation to determine the volume of a solid.

Use an aerial photograph to determine the perimeter and area of the mall; consider other shape permutations.

Student will be able to use integration and differentiation to determine the volume of a solid and see the connection to the formula of a cylinder.
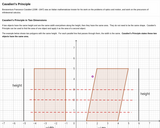
Definition of Cavalieri’s Principle as it applies to two and three dimensional objects, with image examples.
In this lesson, density will be introduced to students by a demonstration of coke verses diet coke. The teacher will then solve density problems for the students on the board. The class will then complete a lab on the density of plastics. After lab the students will compare results. Each group presents a PowerPoint presentation of their results.
This video solves a word problem about the number of passengers a blimp can carry, using knowledge of volume and density.
In this Khan Academy activity, students will answer word problems about density.

Explore flat geometry (Euclidean) that is based on figures on a plane versus spherical geometry (non-Euclidean) that is based on figures on a curved surface.

This lesson unit is intended to help teachers assess how well students are able to solve problems involving area and volume, and in particular, to help you identify and assist students who have difficulties with the following: computing perimeters, areas and volumes using formulas; and finding the relationships between perimeters, areas, and volumes of shapes after scaling.

This lesson plan explores the basic principals behind designing and building a home, and the many variations and unique qualities that go into it. Students will have the opportunity to design their own homes and furniture while understanding coding and planning limitations.
Students create scale drawings of polygonal figures by the Ratio Method.
Given a figure and a scale drawing from the Ratio Method, students answer questions about the scale factor and the center.
Students understand that parallel lines cut transversals into proportional segments. They use ratios between corresponding line segments in different transversals and ratios within line segments on the same transversal.
Students understand Eratosthenes’ method for measuring the earth and solve related problems.
Students understand how the Greeks measured the distance from the earth to the moon and solve related problems.

This packet contains a curriculum-embedded CCLS aligned task and instructional supports. The final task assesses student mastery of the geometry standards related to finding the volume of geometric figures.
Class activity using volume, area and density.

Use remotely sensed data to estimate and measure the area of (center-pivot irrigation) crop circles.

This lesson unit is intended to help teachers assess how well students are able to: choose appropriate mathematics to solve a non-routine problem; generate useful data by systematically controlling variables; and develop experimental and analytical models of a physical situation.

Practice using volume and density when optimizing space and cost

Practice worksheet on population density