This video models a context about lengths of strings and the frequency of their vibrations with an inverse variation equation.
- Subject:
- Mathematics
- Material Type:
- Demonstration
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Date Added:
- 03/01/2018

This video models a context about lengths of strings and the frequency of their vibrations with an inverse variation equation.
Texas Instruments activity that discusses image and preimage.
The purpose of this task is to solve some expressions requiring fractional exponents in an interesting modeling context.

Students will consider and model "exponential decay" and to compare observed data to what is expected under a given model.
This lesson explains how the graph of a function may be shifted to the left or right.

Lesson with videos showing expectations of dilating lines and angles

Unit with systems of equations, including linear and quadratic

This resource introduces Linear-Quadratic Systems of Equations and provides problems of solving them in context.
Students learn to solve a system of linear equations (2 equations with 2 variables) by substitution and elimination methods. They also review the definitions of consistent (independent and dependent) and inconsistent systems, and associate the number of solutions of a system with them.
Here you will learn about "function families," and about two kinds of function families in particular: Linear Functions and Absolute Value Functions.

The purpose of this task is to give students the opportunity to make connections between equations and the geometry of their graphs. They must read information from the graph (such as the vertical intercept of the quadratic graph or the slope of the linear one), use that information to construct and solve an equation, then interpret their solution in terms of the graph. The task also requires the basic understanding that the coordinates of the points of intersection of the graphs are the pairs of values of the variables that solve the system.
This task builds on students' prior knowledge and understanding of conditional probability, and introduces the concept of independence of events.
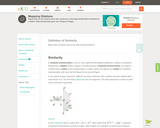
Website with info and videos showing preservation of angles in dilations.
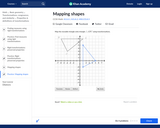
In this Khan Academy activity, students will map a movable shapen to a given shape by using translations, rotations, and/or reflections.
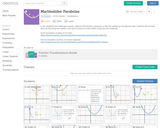
In this lesson, students will be able to: restrict, reposition, and resize parabolas at will using vertex form (y=a(x-h)2+k) and use precision in describing these transformations using words and/or symbols.

Adapted from mathematicsvisionproject.com’s Material Overview:
The Mathematics Vision Project (MVP) was created as a resource for teachers to implement the Common Core State Standards (CCSS) using a task-based approach that leads to skill and efficiency in mathematics by first developing understanding. The MVP approach develops the Standards of Mathematical Practice through experiential learning. Students engage in mathematical problem solving, guided by skilled teachers, in order to achieve mathematical proficiency: conceptual understanding, procedural fluency, strategic competence, adaptive reasoning, and productive disposition. The MVP authors created a curriculum where students do not learn solely by either “internalizing what a teacher or book says or, on the other hand, solely by inventing mathematics on their own.”
The MVP classroom experience begins by confronting students with an engaging problem and allows them to grapple with solving it. As students’ ideas emerge, take form, and are shared, the teacher deliberately orchestrates the student discussions and explorations toward a focused math goal. Students justify their own thinking while clarifying, describing, comparing, and questioning the thinking of others leading to refined thinking and mathematical fluency. What begin as ideas become concepts that lead to formal, traditional math definitions and properties. Strategies become algorithms that lead to procedures supporting efficiency and consistency. Representations become tools of communication which are formalized as mathematical models. Students learn by doing mathematics.

This task addresses the first part of standard F-BF.3: “Identify the effect on the graph of replacing f(x) by f(x)+k, kf(x), f(kx), and f(x+k) for specific values of k (both positive and negative). Here, students are required to understand the effect of replacing x with x+k, but this task can also be modified to test or teach function-building skills involving f(x)+k, kf(x), and f(kx) in a similar manner.

The goal of this task is to use similarity transformations to relate two triangles. The triangles in question are obtained by taking midpoints of two sides of a given triangle.

Practice worksheet on midpoint of triangle segments.
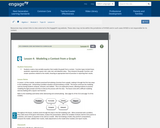
Students create a two-variable equation that models the graph from a context. Function types include linear, quadratic, exponential, square root, cube root, and absolute value. They interpret the graph, function, and answer questions related to the model, choosing an appropriate level of precision in reporting their results