This is a adding and subtracting polynomials assignment that includes an answer key and a QR code for students to check their own work.
- Subject:
- Algebra
- Math 1
- Material Type:
- Homework/Assignment
- Author:
- KORI ELLIOTT
- Date Added:
- 06/01/2020

This is a adding and subtracting polynomials assignment that includes an answer key and a QR code for students to check their own work.
Students are expected to learn how to factor polynomials with an emphasis on quadratic expressions.

This is a visual demonstration of the sector-proof of the formula for the area of circle.

This task explores the real world topic of building light rails. Throughout the implementation of this task the students will learn about the cost of building railways and how to implement them within a budget. This task explores such mathematical concepts of using coordinates to find the distance between points, using coordinates to build polygons and find the area and length of sides, and writing equations of parallel lines.

This lesson unit is intended to help teachers assess how well students are able to create and solve linear equations. In particular, the lesson will help you identify and help students who have the following difficulties: solving equations with one variable and solving linear equations in more than one way.

This lesson unit is intended to help teachers assess how well students are able to classify solutions to a pair of linear equations by considering their graphical representations. In particular, this unit aims to help teachers identify and assist students who have difficulties in: using substitution to complete a table of values for a linear equation; identifying a linear equation from a given table of values; and graphing and solving linear equations.

This lesson unit is intended to help teachers assess how well students are able to interpret exponential and linear functions and in particular to identify and help students who have the following difficulties: translating between descriptive, algebraic and tabular data, and graphical representation of the functions; recognizing how, and why, a quantity changes per unit intervale; and to achieve these goals students work on simple and compound interest problems.
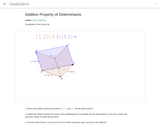
Ana Donevska Todorova Humboldt Universitハt zu Berlin Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftliche Fakultハt II Institut f゚r Mathematik, Didaktik der Mathematik ??? ?????????? ?????? ???????? ?? ???????????? ????? ? ????

Ana Donevska Todorova Humboldt Universitハt zu Berlin Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftliche Fakultハt II Institut f゚r Mathematik, Didaktik der Mathematik

This dynamic worksheet illustrates the relationship between the DETERMINANT, the Area of the pre-image, and the Area of the image.

Ana Donevska Todorova Humboldt Universitハt zu Berlin Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftliche Fakultハt II Institut f゚r Mathematik, Didaktik der Mathematik
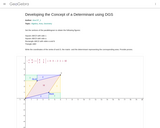
Developing the Concept of a Determinant using DGS

This lesson unit is intended to help assess how well students are able to interpret and use scale drawings to plan a garden layout. This involves using proportional reasoning and metric units.
Calculating time, distance, and speed of falling objects.
EXERCISING IN SPACE
Algebra 1
Key Topic: Slope, linear equations, direct variation, independent and dependent variables, different representations of a function
Students will identify a direct variation, solve linear equations, and create tables based on the exercise equipment provided for astronauts on long duration missions on the International Space Station (ISS) in order to maintain their fitness to perform mission objectives and to return to Earth without serious health complications.
Students will
identify direct variation from ordered pairs by calculating the constant of variation;
calculate slope from two points using the slope formula;
determine independent and dependent variables;
solve linear equations; and
create tables.
Prerequisites: Students should have prior knowledge of direct variation, the constant of variation, linear functions, different representations of a linear function, the properties of a linear function, calculating slope, and solving linear equations.

Students will build their learning on one-step equations. Students will be able to choose what they complete for each section which gives them some variability in their learning. Students are also able to choose between taking a typical test or completing a "more fun" activity such as creating a poster or videoing themself teaching a couple problems. This resource was developed as part of a professional learning opportunity funded by the NCDPI Digital Learning Initiative Planning Grant/

Students will build their learning on combining like terms, distributive property, and combining like terms when using the distributive property. Students will be able to choose what they complete for each section which gives them some variability in their learning. Students are also able to choose between taking a typical test or completing a "more fun" activity such as creating a poster or videoing themself teaching a couple problems. This resource was developed as part of a professional learning opportunity funded by the NCDPI Digital Learning Initiative Planning Grant.
This simulation allows you to use a slider to see how positive and negative integers add on a number line.

A Constructed Response Item provided by Smarter Balanced as preliminary examples of the types of items that students might encounter on the summative assessment. The item prompt students to produce a text or numerical response in order to collect evidence about their knowledge or understanding of writing a function defined by an expression in different but equivalent forms to reveal and explain different properties of a LINEAR function. MAT.HS.CR.1.00FIF.M.274

This lesson unit is intended to help teachers assess how well students are able to understand what the different algebraic forms of a quadratic function reveal about the properties of its graphical representation. In particular, the lesson will help teachers identify and help students who have the following difficulties: understanding how the factored form of the function can identify a graphŐs roots; understanding how the completed square form of the function can identify a graphŐs maximum or minimum point; and understanding how the standard form of the function can identify a graphŐs intercept.